Diabetes Information & Resources
Over 589 million people worldwide have diabetes. What is diabetes, what are the symptoms, and how can you maintain a healthy lifestyle?
What is Diabetes?
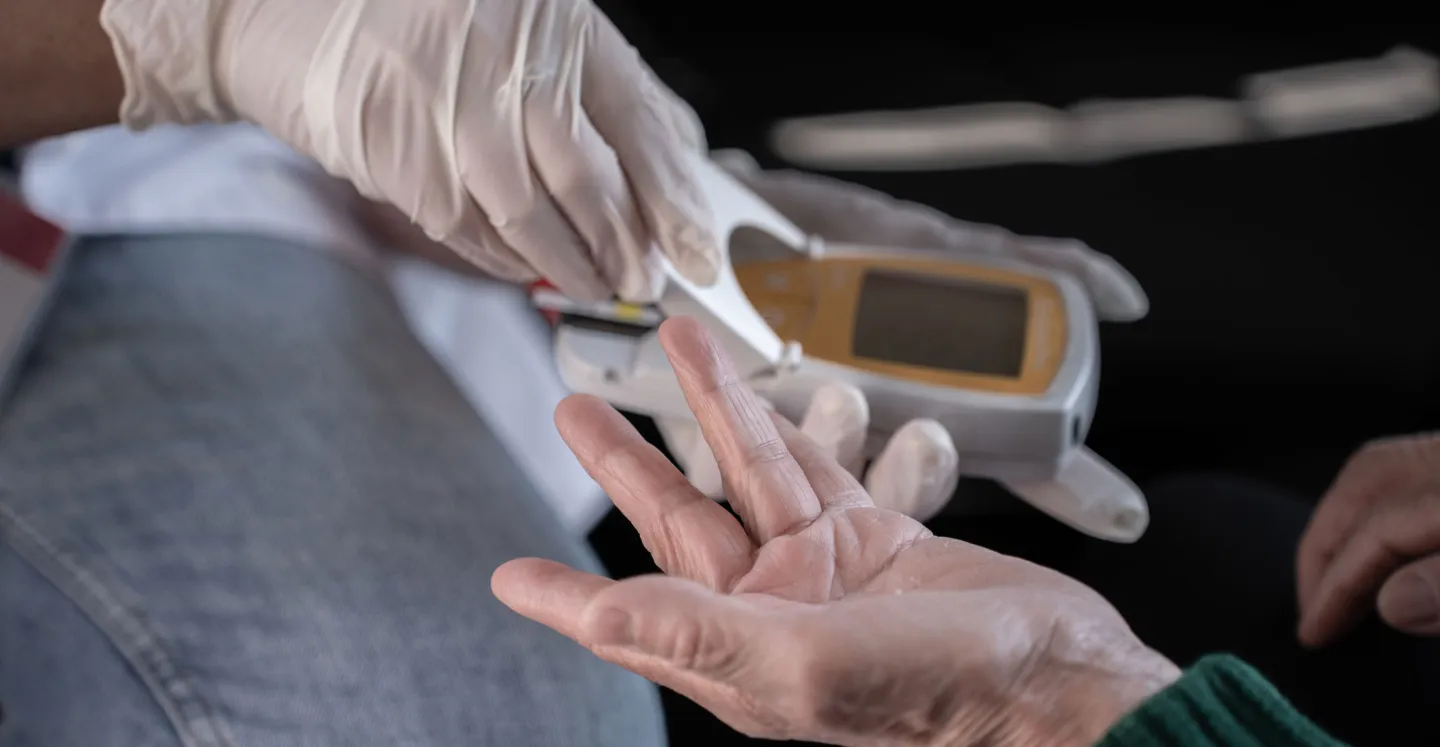
Diabetes is a common medical condition where the blood sugar (glucose) in your body is too high. This occurs when the pancreas is not able to make enough insulin, and your body is reacting to the insufficient or lack of insulin. Diabetes can impact people of all ages and are typically lifelong. With proper medications and lifestyle modifications, one can maintain a healthy life. If not treated properly, diabetes can cause health problems like heart disease, eyesight issues, damage to the kidneys, and damage to the nervous system as it most commonly occurs in childhood.
What are the three main types | What are the symptoms? | 5 Steps to Self-Care
There are other forms of diabetes that are classified as sub-types, or monogenic diabetes. These types of diabetes are more rare and are caused by the contribution of a single gene rather than multiple genes plus environmental factors (Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes) include prediabetes, also called impaired glucose tolerance, which is when your glucose levels are higher than normal.
What are the symptoms of diabetes?
It is important to speak with your health care provider if you experience the following symptoms.
- Lack of energy or fatigue
- Dry mouth and increased thirst
- Constant hunger
- Frequent urination
- Unexplained weight loss
- Blurred vision
- Numbness in hands or feet
- Sores and cuts that take a while to heal
- Frequent yeast infections on the skin
5 Steps to Self-Care
Project HOPE has developed an innovative diabetes self-management course called 5 Steps to Self-Care. This patient-focused, game-based training provides knowledge on diabetes self-management to improve participants’ understanding of diabetes and improve their overall health.

- Committing to lifelong education grounded in basic understanding of physiology and disease progression
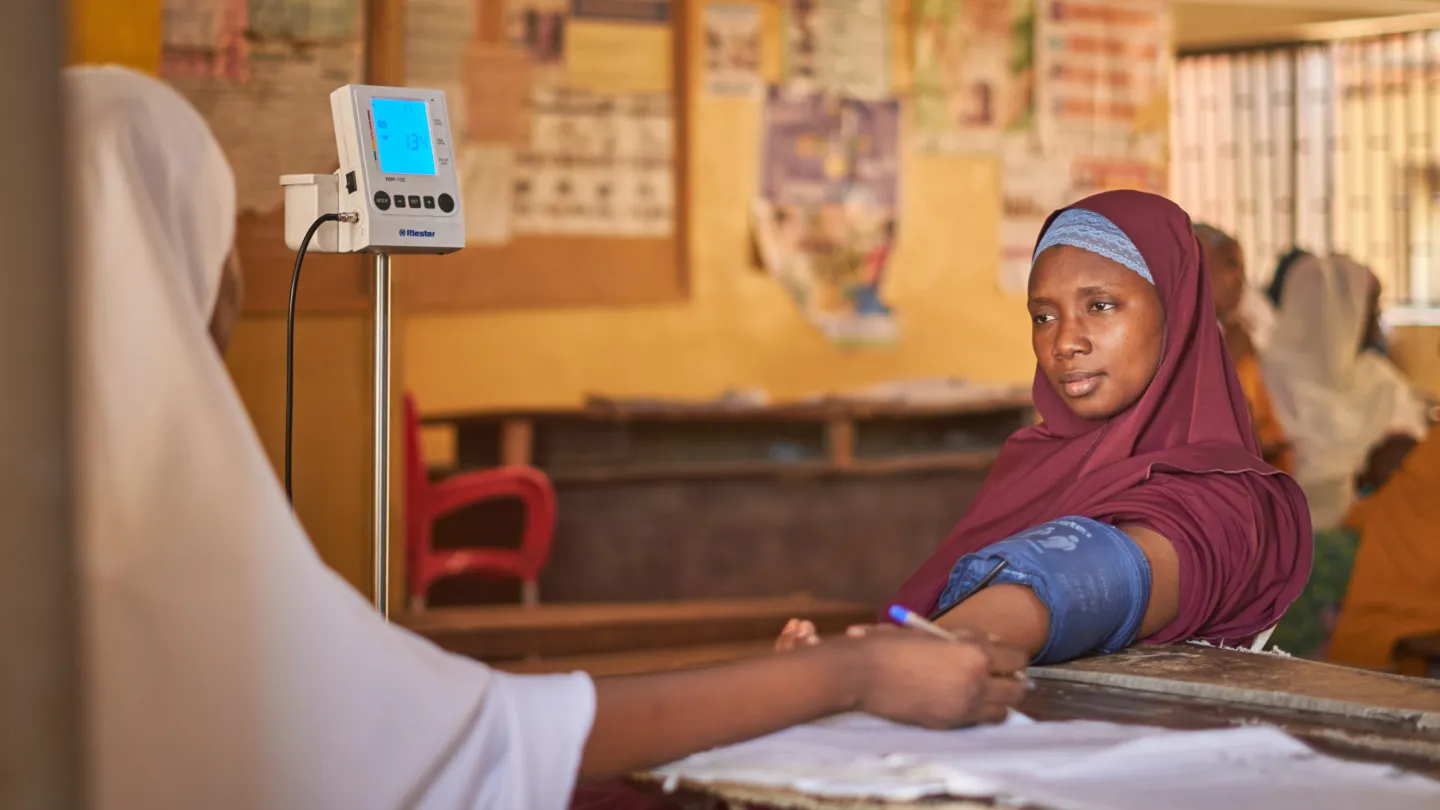
- “Knowing your numbers,” or being able to monitor levels of blood glucose, body mass index, blood pressure, and lipids
- Promoting healthy nutrition to balance carbohydrate, protein, and fat intake
- Making exercise and daily physical activity a regular habit
- Communicating effectively with health professionals for quality care and seeking regular access to specialists and lab work.
The course has been designed to be replicated by primary health care professionals and empowers course graduates to become “peer educators” who share their learnings with friends and family.
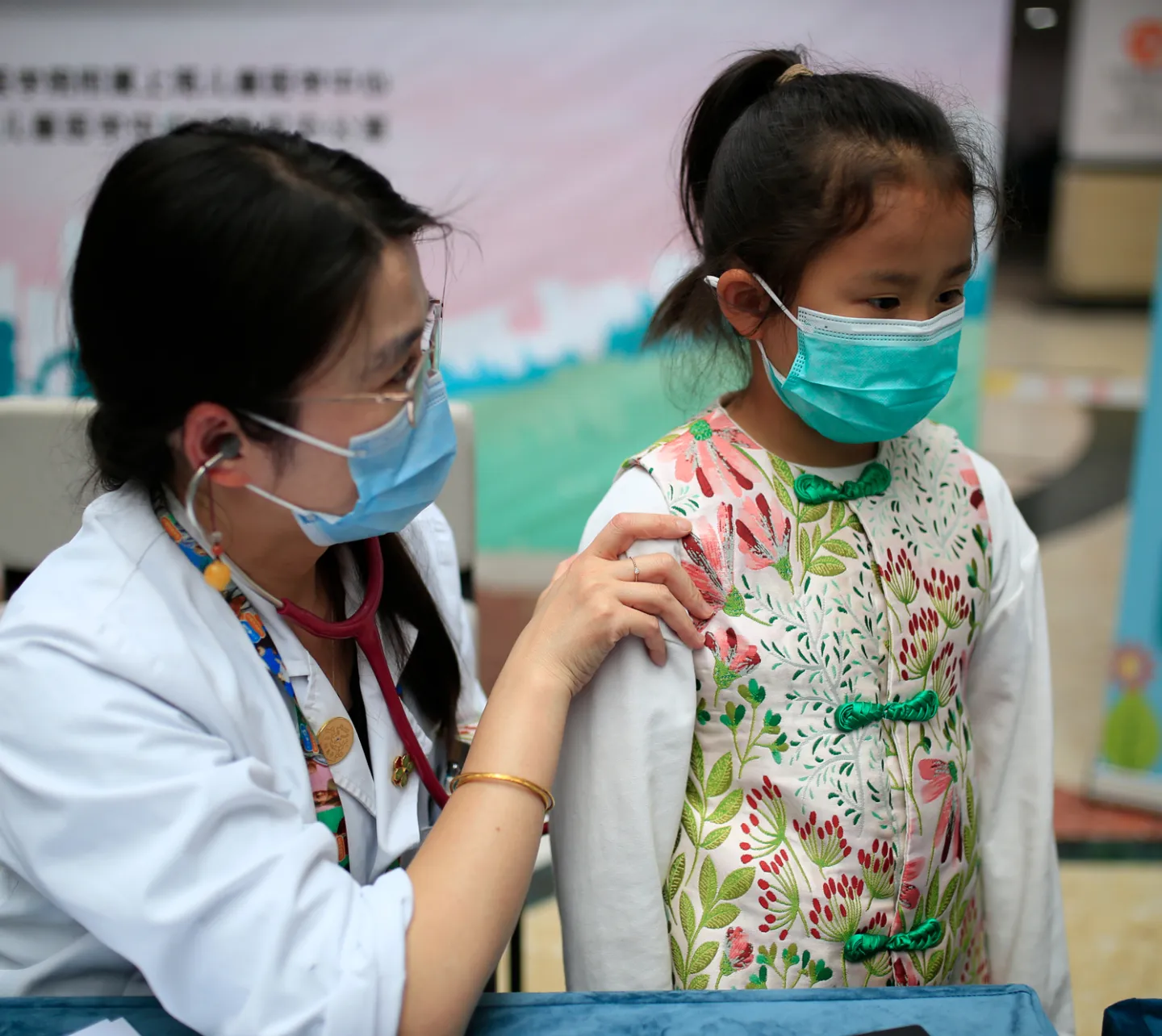

Noncommunicable Diseases
Chronic conditions like heart disease, hypertension, respiratory diseases, and diabetes cause 86% of premature deaths in low- and middle-income countries. Project HOPE has worked to address the source of this glaring health inequity for more than 30 years.